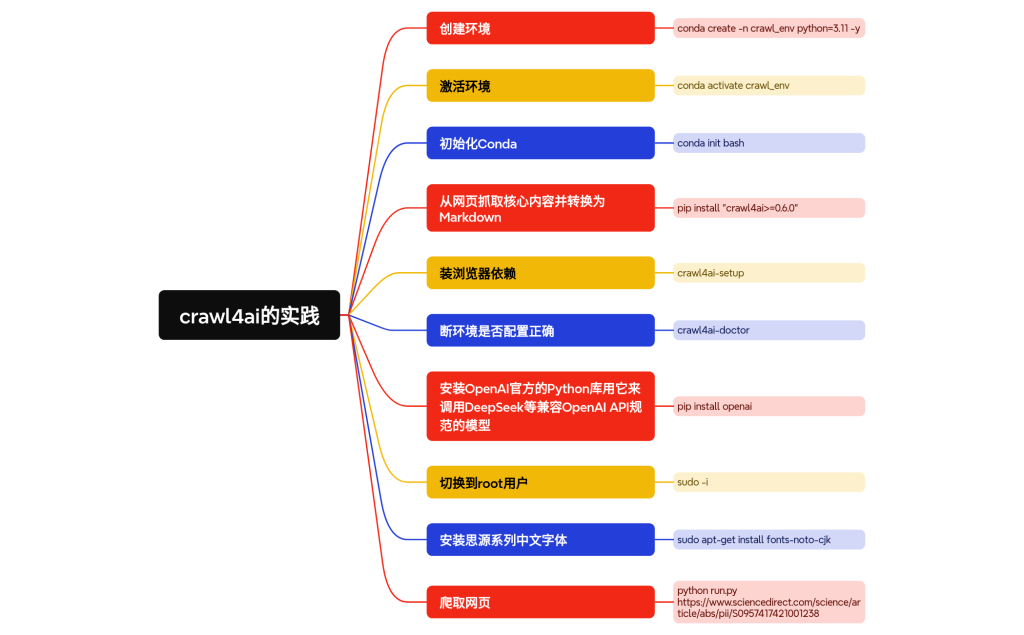
可加V:adoresever
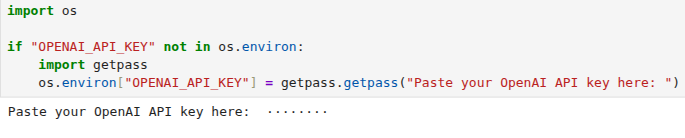
请先在.env文件中设置好 OPENAI_API_KEY
1.extract_tool.py :
“””
通用信息提取工具
使用方法: python extract_tool.py <配置名称> <输入文件>
“””
import langextract as lx
import os
import sys
import argparse
from datetime import datetime
from pathlib import Path
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from collections import Counter
# 导入配置
from config import EXTRACTION_CONFIGS
# 自动加载 .env 文件,同时加载 OPENAI_API_KEY 和 LANGEXTRACT_API_KEY
load_dotenv()
def process_document(config_name, input_file):
“””
根据配置处理文件 (已整合所有成功秘诀)
“””
# — 1. 配置和文件检查 —
if config_name not in EXTRACTION_CONFIGS:
print(f”❌ 错误: 未找到配置 ‘{config_name}'”)
sys.exit(1)
if not Path(input_file).exists():
print(f”❌ 错误: 文件不存在 ‘{input_file}'”)
sys.exit(1)
config = EXTRACTION_CONFIGS[config_name]
print(“-” * 50)
print(f”📁 处理文件: {input_file} | ⚙️ 配置: {config_name}”)
print(f”📝 任务描述: {config.get(‘description’, ‘无描述’)}”)
with open(input_file, ‘r’, encoding=’utf-8′) as f:
text = f.read()
print(f”📄 文件长度: {len(text):,} 字符”)
# — 2. 构建提取参数 —
model_id = config.get(“model”, “gpt-4o-mini”)
extract_params = {
“text_or_documents”: text,
“prompt_description”: config[“prompt”],
“examples”: config[“examples”],
“model_id”: model_id,
“extraction_passes”: config.get(“extraction_passes”, 1),
“max_workers”: config.get(“max_workers”, 10),
“max_char_buffer”: config.get(“max_char_buffer”, 2000)
}
# — 3. 针对不同模型应用特殊配置 (核心秘诀) —
if ‘gpt’ in model_id.lower():
print(f”🔧 检测到 OpenAI 模型 ({model_id}),应用特殊配置…”)
from langextract.inference import OpenAILanguageModel
api_key = os.environ.get(“OPENAI_API_KEY”)
if not api_key:
print(“\n❌ 致命错误: 未在 .env 文件中找到 ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’。”)
print(” 请在 .env 文件中添加一行: OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-…”)
sys.exit(1)
extract_params.update({
“language_model_type”: OpenAILanguageModel,
“api_key”: api_key,
“fence_output”: True,
“use_schema_constraints”: False
})
else:
# 默认使用 Gemini 或其他模型,langextract 会自动寻找 LANGEXTRACT_API_KEY
print(f”🔧 使用默认或 Gemini 模型 ({model_id}) 配置…”)
api_key = os.environ.get(“LANGEXTRACT_API_KEY”)
if not api_key:
print(f”\n❌ 致命错误: 未找到适用于 ‘{model_id}’ 的 API 密钥。”)
print(” 请在 .env 文件中添加: LANGEXTRACT_API_KEY=…”)
sys.exit(1)
# — 4. 执行提取 —
print(“🚀 开始提取,请耐心等待…”)
result = lx.extract(**extract_params)
if not result.extractions:
print(“\n⚠️ 警告:本次运行未能提取到任何实体。”)
print(” 请检查: 1. Prompt和示例是否清晰。 2. API密钥和账户额度。 3. 源文件内容是否匹配任务。”)
return
# — 5. 保存和可视化 (使用最新、正确的方式) —
output_dir = Path(“extraction_results”)
output_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime(“%Y%m%d_%H%M%S”)
output_base_name = f”{config_name}_{Path(input_file).stem}_{timestamp}”
jsonl_path = output_dir / f”{output_base_name}.jsonl”
lx.io.save_annotated_documents([result], output_name=str(jsonl_path.name), output_dir=str(output_dir))
html_path = output_dir / f”{output_base_name}.html”
html_content = lx.visualize(str(jsonl_path))
with open(html_path, “w”, encoding=”utf-8″) as f:
f.write(html_content)
print(“\n✅ 提取完成!”)
print(f” • 数据文件: {jsonl_path}”)
print(f” • 可视化报告: {html_path}”)
# — 6. 结果统计 —
class_counts = Counter(e.extraction_class for e in result.extractions)
print(“\n📊 提取统计:”)
print(f” 总实体数: {len(result.extractions)}”)
for class_name, count in sorted(class_counts.items()):
print(f” – {class_name}: {count} 个”)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=”通用信息提取工具 (最终增强版)”)
parser.add_argument(“config_name”, help=”配置名称 (如 medical, fable 等)”)
parser.add_argument(“input_file”, help=”输入文件路径”)
args = parser.parse_args()
process_document(args.config_name, args.input_file)
if __name__ == “__main__”:
main()
2.config.py :
“””
信息提取配置文件
在这里定义不同类型文档的提取规则
“””
import langextract as lx
# 提取配置字典
EXTRACTION_CONFIGS = {
# ========== 医疗记录配置 ==========
“medical”: {
“description”: “提取医疗记录中的药物、诊断和治疗信息”,
“model”: “gpt-4o-mini”, # 可选: gpt-4o, gpt-4, gpt-3.5-turbo
“extraction_passes”: 2, # 多轮提取提高准确率
“max_workers”: 10,
“max_char_buffer”: 1500,
“prompt”: “””
提取以下医疗信息:
1. 药物名称、剂量、用药频率、用药途径
2. 诊断结果
3. 症状描述
4. 治疗方案
使用原文精确提取,不要改写或总结。
为每个实体提供相关属性。
“””,
“examples”: [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text=”患者主诉头痛3天,诊断为偏头痛。处方:布洛芬400mg,口服,每日3次,饭后服用。”,
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”症状”,
extraction_text=”头痛3天”,
attributes={“持续时间”: “3天”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”诊断”,
extraction_text=”偏头痛”,
attributes={“类型”: “神经系统疾病”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”药物”,
extraction_text=”布洛芬”,
attributes={
“剂量”: “400mg”,
“途径”: “口服”,
“频率”: “每日3次”,
“注意事项”: “饭后服用”
}
),
]
)
]
},
# ========== 合同文件配置 ==========
“contract”: {
“description”: “提取合同中的关键条款和信息”,
“model”: “gpt-4o-mini”, # 合同一般比较规范,可以用便宜的模型
“extraction_passes”: 1,
“max_workers”: 5,
“max_char_buffer”: 2000,
“prompt”: “””
提取合同中的以下信息:
1. 甲方和乙方信息(公司名称、代表人)
2. 合同金额和支付条款
3. 合同期限和重要日期
4. 主要权利和义务
5. 违约条款
保持原文的准确性,提取完整条款。
“””,
“examples”: [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text=”甲方:北京科技有限公司(法定代表人:张明),乙方:上海贸易有限公司,合同总金额:人民币100万元整,合同期限:2024年1月1日至2024年12月31日。”,
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”甲方”,
extraction_text=”北京科技有限公司”,
attributes={“法定代表人”: “张明”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”乙方”,
extraction_text=”上海贸易有限公司”,
attributes={}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”金额”,
extraction_text=”人民币100万元整”,
attributes={“币种”: “人民币”, “数额”: “100万元”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”期限”,
extraction_text=”2024年1月1日至2024年12月31日”,
attributes={“开始日期”: “2024年1月1日”, “结束日期”: “2024年12月31日”}
),
]
)
]
},
# ========== 新闻文章配置 ==========
“news”: {
“description”: “提取新闻文章的关键要素”,
“model”: “gpt-4o-mini”,
“extraction_passes”: 1,
“max_workers”: 15,
“max_char_buffer”: 2500,
“prompt”: “””
提取新闻文章中的:
1. 人物(姓名、职位、所属机构)
2. 地点
3. 时间
4. 事件(发生了什么)
5. 引用的言论
标注每个事件的重要性(高/中/低)。
“””,
“examples”: [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text=”昨天下午,苹果公司CEO库克在加州总部宣布,公司将投资50亿美元开发AI技术。他表示:’这是苹果历史上最重要的战略转型。'”,
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”时间”,
extraction_text=”昨天下午”,
attributes={“精确度”: “相对时间”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”人物”,
extraction_text=”库克”,
attributes={“职位”: “CEO”, “公司”: “苹果公司”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”地点”,
extraction_text=”加州总部”,
attributes={“类型”: “公司总部”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”事件”,
extraction_text=”投资50亿美元开发AI技术”,
attributes={“重要性”: “高”, “金额”: “50亿美元”, “领域”: “AI技术”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”言论”,
extraction_text=”这是苹果历史上最重要的战略转型”,
attributes={“发言人”: “库克”, “态度”: “积极”}
),
]
)
]
},
# ========== 学术论文配置 ==========
“academic”: {
“description”: “提取学术论文的关键信息”,
“model”: “gpt-4o-mini”,
“extraction_passes”: 2,
“max_workers”: 10,
“max_char_buffer”: 3000,
“prompt”: “””
提取学术论文中的:
1. 研究问题和假设
2. 研究方法
3. 主要发现和结论
4. 引用的重要文献
5. 数据和统计结果
保持学术术语的准确性。
“””,
“examples”: [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text=”本研究采用随机对照试验(RCT)方法,样本量n=500,结果显示治疗组相比对照组症状改善率提高了35% (p<0.001)。",
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”方法”,
extraction_text=”随机对照试验(RCT)”,
attributes={“类型”: “实验研究”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”样本”,
extraction_text=”n=500″,
attributes={“样本量”: “500”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”结果”,
extraction_text=”症状改善率提高了35%”,
attributes={“改善幅度”: “35%”, “统计显著性”: “p<0.001"}
),
]
)
]
},
# ========== 客户反馈配置 ==========
“feedback”: {
“description”: “提取客户反馈中的情感和问题”,
“model”: “gpt-3.5-turbo”,
“extraction_passes”: 1,
“max_workers”: 20,
“max_char_buffer”: 1000,
“prompt”: “””
提取客户反馈中的:
1. 情感倾向(正面/负面/中性)
2. 产品或服务名称
3. 具体问题或建议
4. 客户需求
为每个提取内容标注情感强度(1-5分)。
“””,
“examples”: [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text=”你们的客服态度太差了!我打了3次电话都没解决问题,产品质量倒是不错,就是售后服务需要改进。”,
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”负面情感”,
extraction_text=”客服态度太差了”,
attributes={“对象”: “客服”, “强度”: “5”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”问题”,
extraction_text=”打了3次电话都没解决问题”,
attributes={“频次”: “3次”, “状态”: “未解决”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”正面情感”,
extraction_text=”产品质量倒是不错”,
attributes={“对象”: “产品质量”, “强度”: “3”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”建议”,
extraction_text=”售后服务需要改进”,
attributes={“改进点”: “售后服务”}
),
]
)
]
},
# ========== 文学作品配置 ==========
“literary”: {
“description”: “提取文学作品(如小说、诗歌、戏剧)中的核心元素”,
“model”: “gpt-4o-mini”, # 文学分析需要更强的理解能力
“extraction_passes”: 2, # 多轮提取以捕捉深层含义
“max_workers”: 10,
“max_char_buffer”: 3000,
“prompt”: “””
提取文学作品中的以下要素:
1. 主要人物 (姓名、角色、性格特点)
2. 场景和氛围 (地点、时间、环境描述、情感基调)
3. 关键情节 (发生了什么,转折点)
4. 主题思想 (作品探讨的核心议题,如爱、死亡、成长、社会批判等)
5. 象征或意象 (具有特殊含义的物品或概念,如“红灯笼”象征压抑)
6. 修辞手法 (如比喻、拟人、排比等)
请精确引用原文,并为每个提取项提供相关属性。
“””,
“examples”: [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text=”我冒着严寒,回到相隔二千余里,别了二十余年的故乡去。时候既然是深冬,渐近故乡时,天气又阴晦了,冷风吹进船舱中,呜呜的响,从篷隙向外一望,苍黄的天底下,远近横着几个萧索的荒村,没有一些活气。”,
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”关键情节”,
extraction_text=”回到…故乡去”,
attributes={“事件类型”: “返乡”, “人物”: “我”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”场景”,
extraction_text=”相隔二千余里,别了二十余年的故乡”,
attributes={“地点”: “故乡”, “时间跨度”: “二十余年”, “距离”: “二千余里”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”氛围”,
extraction_text=”萧索的荒村,没有一些活气”,
attributes={“情感基调”: “荒凉、衰败”, “天气”: “严寒, 阴晦”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”意象”,
extraction_text=”苍黄的天”,
attributes={“色彩”: “苍黄”, “暗示”: “压抑、沉闷”}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class=”修辞手法”,
extraction_text=”冷风吹进船舱中,呜呜的响”,
attributes={“类型”: “拟声/拟人”, “对象”: “冷风”}
),
]
)
]
},
}
# ========== 添加你自己的配置 ==========
# 复制上面的模板,修改为你需要的提取规则
# “your_config”: {
# “description”: “你的配置描述”,
# “model”: “gpt-4o-mini”,
# “prompt”: “你的提取指令…”,
# “examples”: […]
# }